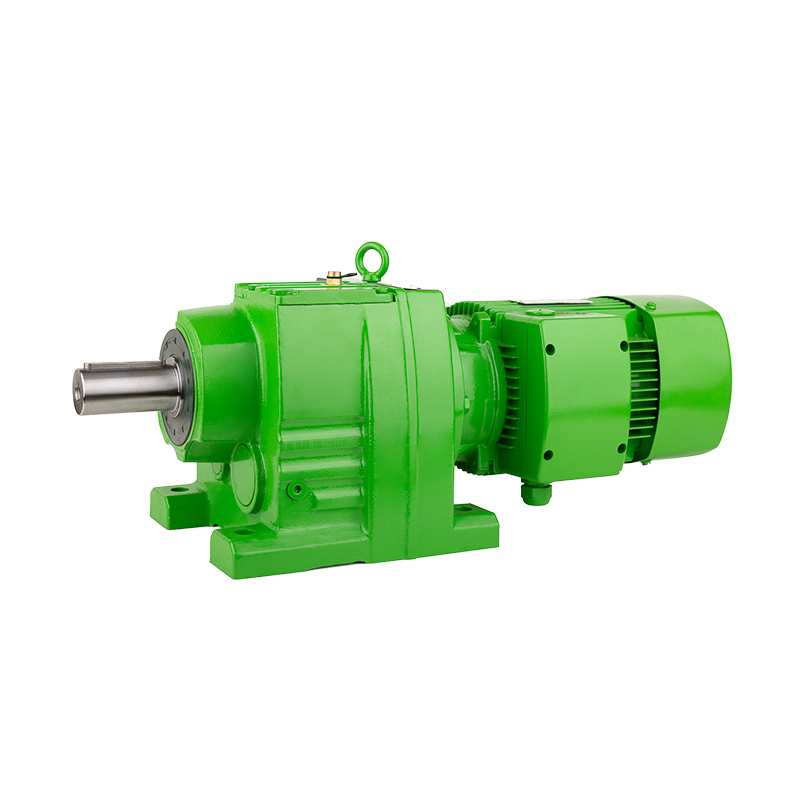

The r series helical geared motor has become a pivotal choice in many industrial applications due to its versatility, efficiency, and robust design. One of the most important technical considerations when selecting an r series helical geared motor is the gear ratio, which significantly affects the performance, torque output, and speed of the motor system.
Understanding the concept of gear ratio in r series helical geared motors
A gear ratio refers to the ratio between the input speed of the motor and the output speed of the gearbox. In an r series helical geared motor, gear ratios determine the torque multiplication and speed reduction that the motor can achieve. Selecting the correct gear ratio is essential for optimizing efficiency, minimizing wear, and ensuring that the motor meets the operational requirements of a specific application.
The r series helical geared motor is designed to handle a range of gear ratios, allowing flexibility across different industrial scenarios. This adaptability makes it suitable for applications ranging from conveyors and packaging machinery to heavy-duty material handling systems.
Common gear ratios available in r series helical geared motors
The r series helical geared motor is manufactured with a variety of gear ratio options to accommodate different operational demands. Typically, gear ratios can range from single-stage ratios of 3:1 to 10:1 to multi-stage ratios exceeding 100:1. This range allows precise matching of the motor’s output speed to the mechanical requirements of the driven equipment.
Table 1: Example gear ratio options for r series helical geared motors
| Stage Type | Gear Ratio Range | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Single-stage | 3:1 – 10:1 | Light-duty conveyors, fans |
| Two-stage | 10:1 – 50:1 | Packaging machines, mixers |
| Multi-stage | 50:1 – 100+:1 | Heavy-duty conveyors, extruders |
These ratios illustrate the flexibility of the r series helical geared motor, enabling engineers to balance speed and torque according to the specific application requirements.
Factors influencing gear ratio selection
When choosing a gear ratio for an r series helical geared motor, several critical factors must be considered:
Application load requirements
The type of load the motor will drive plays a significant role in determining the appropriate gear ratio. Heavy or fluctuating loads often require higher gear ratios to ensure sufficient torque output while maintaining efficiency.
Desired output speed
The operational speed of the driven machinery dictates the gear ratio selection. For high-speed applications, a lower gear ratio may be preferable, while for precise, low-speed operations, higher gear ratios are typically required.
Space constraints and installation
Physical dimensions of the equipment and available installation space can influence gear ratio selection. Multi-stage gearboxes can achieve high ratios without excessively increasing the size of the r series helical geared motor.
Efficiency and energy consumption
Gear ratios affect the efficiency of the motor. An optimal ratio ensures that the motor operates within its ideal efficiency range, minimizing energy consumption while delivering the required torque.
Advantages of using variable gear ratios in r series helical geared motors
One of the significant benefits of the r series helical geared motor is the availability of multiple gear ratios, providing several operational advantages:
- Flexibility in application: Different gear ratios allow the motor to adapt to a wide range of mechanical requirements.
- Optimized torque output: Correct gear ratios maximize torque while minimizing stress on mechanical components.
- Energy efficiency: Matching gear ratios to load conditions helps reduce unnecessary energy consumption.
- Extended motor life: Proper ratio selection reduces wear and tear, contributing to longer operational lifespan.
Industry applications and gear ratio considerations
The r series helical geared motor finds extensive use across industries where reliable torque and controlled speed are critical. Examples include:
- Material handling and conveyors: Higher gear ratios are often used for heavy loads requiring precise control.
- Packaging machinery: Medium gear ratios balance speed and torque for efficient production lines.
- Mixers and agitators: Multi-stage gear ratios provide high torque at low speeds for consistent mixing results.
- Printing presses and assembly lines: Variable gear ratios allow customization to specific operational cycles.
Selecting the correct gear ratio is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring consistent output across these diverse applications.
Gear ratio customization in r series helical geared motors
Many manufacturers of r series helical geared motors offer customization of gear ratios to meet specific operational demands. This customization can involve:
- Adjusting the number of stages: Adding or removing gear stages to achieve a desired speed reduction.
- Custom tooth profiles: Optimizing gear engagement for specific torque and noise requirements.
- Housing modifications: Adapting the motor size or mounting configuration to accommodate unique gear ratios.
Such customization ensures that industrial users can achieve the best balance between performance, efficiency, and space utilization.
Maintenance and monitoring considerations related to gear ratios
Proper maintenance of an r series helical geared motor is crucial, particularly when operating at extreme gear ratios. Higher ratios can result in increased torque and stress, necessitating regular inspection and lubrication of the gears and bearings. Industrial buyers should consider:
- Lubrication schedules: Ensuring optimal lubrication for all gear stages.
- Temperature monitoring: High gear ratios may generate additional heat.
- Noise and vibration checks: Identifying potential gear wear early to prevent operational disruptions.
By maintaining the r series helical geared motor according to these guidelines, operators can ensure consistent performance and long service life.
 05 Jun,2025
05 Jun,2025