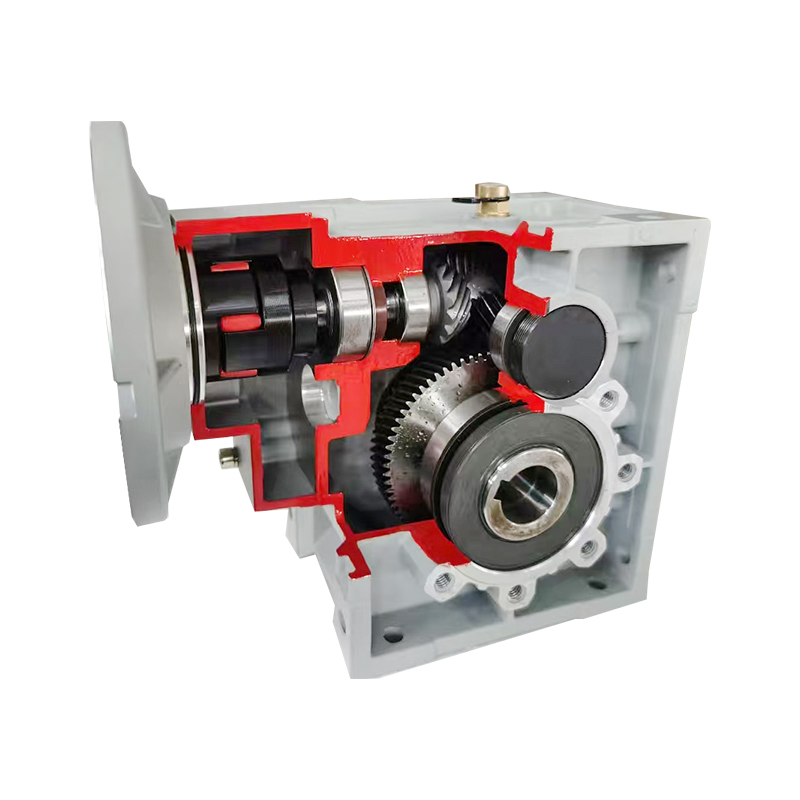

Proper maintenance of a bkm hypoid gear reducer is essential to ensure long-term performance, operational efficiency, and reliability.
Importance of regular maintenance
A bkm hypoid gear reducer is a complex mechanical system designed to transmit torque efficiently while accommodating angular displacement between input and output shafts. Over time, operational stress, environmental factors, and usage conditions can impact the performance of the reducer. Regular maintenance ensures that all components operate within their designed tolerances, reduces unexpected failures, and maintains consistent output torque and speed.
Neglecting maintenance can lead to excessive wear, increased operational noise, reduced energy efficiency, and potential safety hazards. Therefore, a structured maintenance plan tailored to the specific application of the bkm hypoid gear reducer is crucial.
Inspection of lubrication systems
Lubrication type and selection
The bkm hypoid gear reducer relies heavily on effective lubrication to minimize friction and prevent excessive heat buildup. Depending on operating conditions, users may select high-quality gear oils or synthetic lubricants specifically formulated for hypoid gear systems. Lubrication quality directly affects the wear resistance of gears, bearings, and seals.
Oil level and replacement intervals
Maintaining the correct oil level is fundamental. Low lubricant levels can cause overheating and surface damage, whereas overfilling can create unnecessary pressure, leading to seal failure. Regular oil inspections should follow the manufacturer’s recommendations, typically ranging from 3 to 12 months, depending on operational load, environment, and temperature.
Table 1: Recommended lubrication intervals for bkm hypoid gear reducer
| Operating Condition | Oil Type | Inspection Interval | Replacement Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal industrial load | Mineral-based gear oil | Monthly | 12 months |
| Heavy-duty or continuous | Synthetic gear oil | Biweekly | 6 months |
| High-temperature operation | High-temperature oil | Weekly | 3 months |
Signs of lubricant degradation
Users should monitor for darkening of oil, presence of metallic particles, or unusual odors, all of which indicate degradation or contamination. Routine oil analysis can help detect early-stage issues, allowing corrective measures before major damage occurs.
Visual and mechanical inspections
Gear and shaft condition
Periodic inspection of gears and shafts is essential for detecting early signs of misalignment, pitting, or spalling. Observing for unusual vibration or increased backlash can indicate wear that requires attention. BKM hypoid gear reducer gears should maintain smooth meshing and precise alignment to ensure efficient torque transfer.
Bearing and seal integrity
Bearings and seals are critical components that support shaft rotation and prevent lubricant leakage. Regular checks for unusual noise, temperature rise, or visible oil leaks can prevent catastrophic failure. Bearings showing signs of wear, such as metallic scraping or axial play, should be replaced promptly.
Table 2: Key inspection points for bkm hypoid gear reducer
| Component | Inspection Method | Frequency | Indicators of Wear or Failure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gears | Visual and tactile inspection | Every 6 months | Pitting, spalling, uneven wear |
| Bearings | Noise check, vibration analysis | Quarterly | Excessive play, abnormal vibration |
| Seals | Visual inspection | Monthly | Oil leakage, hardened or cracked seals |
| Housing | Surface check | Biannual | Cracks, corrosion, or deformation |
Temperature monitoring
Operational temperature is a key indicator of bkm hypoid gear reducer health. Excessive heat can degrade lubricant, reduce gear strength, and shorten bearing life. Infrared thermography or built-in temperature sensors can provide real-time monitoring. Any sustained temperature above recommended limits should prompt immediate inspection.
Vibration analysis
Vibration analysis is a non-invasive method to assess the internal condition of the bkm hypoid gear reducer. Changes in vibration frequency or amplitude can indicate misalignment, unbalanced loads, or bearing defects. Implementing a predictive maintenance program using vibration monitoring can prevent unexpected downtime and costly repairs.
Cleaning and environmental control
Maintaining a clean operational environment extends the service life of the bkm hypoid gear reducer. Dust, debris, or corrosive agents can contaminate lubrication and accelerate wear. Regular cleaning of the exterior, ventilation openings, and protective covers is recommended. Additionally, humidity control and temperature regulation in the installation area can reduce corrosion and thermal stress.
Load management
Overloading is a common cause of premature failure. Operators should ensure that the bkm hypoid gear reducer is operated within its rated torque and speed specifications. Variable load conditions should be carefully managed, and protective devices such as torque limiters or safety clutches can prevent damage under abnormal conditions.
Scheduled maintenance checklist
A structured checklist ensures all critical maintenance aspects are addressed systematically. Key items include:
- Oil level and quality inspection
- Gear and bearing visual inspection
- Seal condition assessment
- Temperature and vibration monitoring
- Cleaning of housing and ventilation paths
- Verification of mounting and alignment
This approach reduces the risk of missing critical signs of wear or failure.
Documentation and maintenance records
Keeping accurate maintenance records for each bkm hypoid gear reducer allows tracking of wear patterns, oil change history, and repairs. This documentation supports predictive maintenance and facilitates troubleshooting, warranty claims, and compliance with safety regulations.
Best practices for extending lifespan
In addition to routine maintenance, several practices contribute to the long-term reliability of bkm hypoid gear reducer systems:
- Using high-quality lubricants appropriate for operational conditions
- Avoiding frequent start-stop cycles under high load
- Ensuring proper alignment during installation
- Implementing protective covers in harsh environments
- Scheduling periodic professional inspections
Conclusion
Maintaining a bkm hypoid gear reducer requires a comprehensive approach that combines lubrication management, mechanical inspection, environmental control, and operational monitoring.
FAQ
Q1: How often should the oil in a bkm hypoid gear reducer be replaced?
Oil replacement frequency depends on operational conditions. Typically, normal industrial load requires replacement every 12 months, while heavy-duty or high-temperature applications may require more frequent changes.
Q2: What are the signs of bearing failure in a bkm hypoid gear reducer?
Indicators include unusual noise, increased vibration, temperature rise, and excessive play. Prompt inspection and replacement are recommended to avoid major damage.
Q3: Can a bkm hypoid gear reducer operate in high-humidity environments?
Yes, but precautions such as protective seals, humidity control, and regular inspections are necessary to prevent corrosion and lubricant contamination.
Q4: What maintenance methods can prevent gear wear?
Maintaining proper lubrication, checking alignment, controlling load conditions, and monitoring operating temperature are key to preventing gear pitting and spalling.
Q5: Is vibration analysis necessary for all bkm hypoid gear reducers?
While not mandatory for all applications, vibration analysis is highly recommended in critical or high-load industrial systems to detect early signs of wear or imbalance.
References
- Smith, J. Industrial Gear Maintenance and Lubrication Techniques, 2020.
- Brown, R. Hypoid Gear Systems in Modern Machinery, 2019.
- International Standards Organization, ISO 6336: Calculation of Load Capacity of Gears, 2021.
 05 Jun,2025
05 Jun,2025