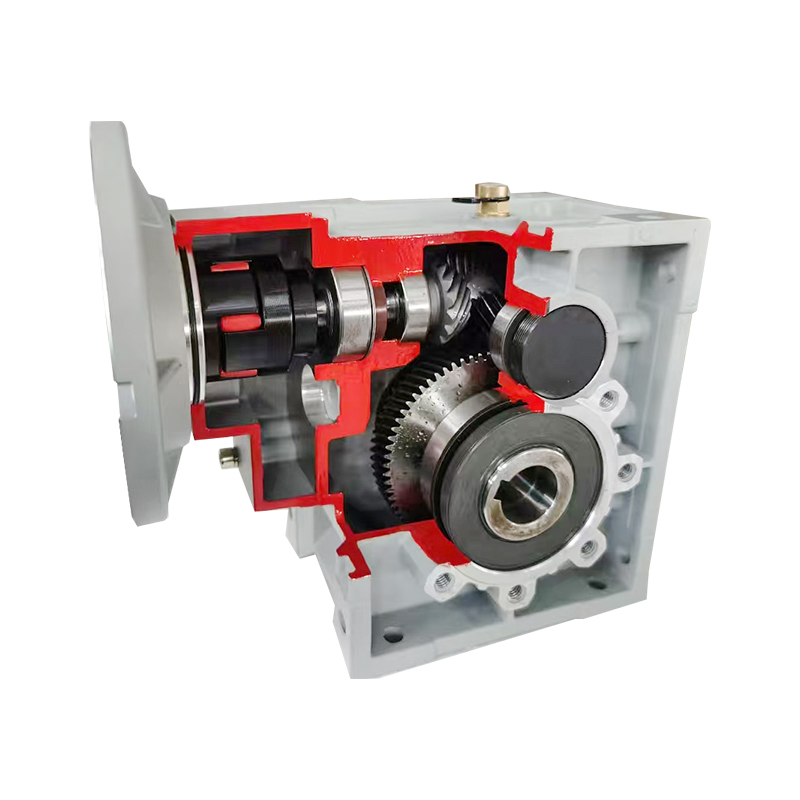

The BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer plays a critical role in mechanical transmission systems across a variety of industrial applications. Efficiency, in this context, is a measure of how effectively the gear reducer converts input energy into useful output while minimizing losses.
Design and Gear Geometry
The design of a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer is one of the most significant factors impacting its efficiency. Hypoid gears feature an offset between the axes of the input and output shafts, which allows for higher torque transmission and smoother operation. However, the geometry of the gears influences the way power is transmitted and can introduce frictional losses if not properly optimized.
Key aspects of design affecting efficiency include:
- Gear tooth profile: The contact pattern between the hypoid pinion and gear must be precise. Improper alignment can increase sliding friction, leading to higher energy loss.
- Tooth surface finish: Smoother surfaces reduce micro-friction between the teeth, improving the mechanical efficiency.
- Offset and angle design: The spiral angle and offset between shafts affect the sliding motion. Larger offsets increase sliding distance and may reduce efficiency if lubrication is insufficient.
Efficient BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer design balances torque capability, smoothness, and minimal friction, resulting in reliable power transmission.
Material Selection and Hardening
Material choice and heat treatment significantly impact the performance and efficiency of a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer. High-quality steel alloys with controlled hardness levels are commonly used to withstand wear and load stress.
Material and surface treatments influence efficiency in the following ways:
- Hardening techniques: Carburizing or induction hardening can create durable tooth surfaces that resist deformation and maintain precise contact.
- Wear resistance: Materials with higher wear resistance reduce the likelihood of tooth pitting and energy loss over time.
- Elastic properties: Appropriate stiffness in the gear material minimizes flexing under load, ensuring consistent power transfer without extra energy consumption.
Selecting appropriate materials and treatments ensures that the BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer maintains efficiency over long operational cycles.
Lubrication and Friction Control
Friction between gear surfaces is a primary source of energy loss in a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer. Lubrication is therefore critical to achieving high efficiency. The type, quality, and maintenance of lubricants directly impact performance.
Considerations include:
- Lubricant type: Gear oils with high-pressure additives reduce friction and wear. Synthetic oils often offer better stability and longer life.
- Lubricant viscosity: Correct viscosity ensures proper film formation between contacting surfaces. Too high viscosity increases drag, while too low viscosity reduces protection.
- Maintenance schedule: Regular inspection and replacement of lubricants prevent efficiency loss caused by contamination, degradation, or insufficient lubrication.
Proper lubrication minimizes sliding friction, reduces heat generation, and extends the operational life of the BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer.
Operating Conditions and Load
The efficiency of a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer also depends on the conditions under which it operates. Deviations from optimal operating parameters can introduce additional losses.
Factors related to operating conditions include:
- Load variations: Gear reducers operating below or above their designed load may experience increased energy losses. Consistent, well-matched loading promotes efficient operation.
- Speed ranges: Operating at excessively high or low speeds outside the design range can reduce gear contact efficiency and increase friction.
- Environmental factors: Temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to dust or contaminants may affect lubricant performance and gear surface conditions.
Monitoring and controlling these operational variables help maintain consistent efficiency in industrial environments.
Alignment and Mounting
Precision alignment between the driving and driven shafts is essential for minimizing energy loss in a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer. Misalignment increases contact stress, friction, and wear, reducing efficiency.
Key alignment considerations:
- Shaft alignment: Proper installation ensures the pinion and gear maintain an optimal contact pattern.
- Mounting rigidity: Secure and vibration-free mounting prevents deflection, which can alter tooth engagement.
- Adjustment mechanisms: Some industrial setups incorporate shims or alignment guides to fine-tune positioning during installation and maintenance.
Accurate alignment reduces unnecessary sliding and improves the transmission efficiency of the BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer.
Heat Generation and Thermal Management
Friction and mechanical load in a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer produce heat, which can affect efficiency. Excessive heat leads to lubricant degradation, material expansion, and increased internal resistance.
Thermal management strategies include:
- Cooling systems: Fans, fins, or external coolers dissipate heat effectively in high-load applications.
- Lubricant selection: Thermally stable oils maintain viscosity under elevated temperatures, ensuring continuous protection.
- Monitoring: Temperature sensors and regular inspections prevent overheating, which can otherwise reduce efficiency and damage components.
Maintaining proper operating temperatures ensures the BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer continues to operate efficiently under varying conditions.
Maintenance Practices
Regular and systematic maintenance is a critical factor in sustaining the efficiency of a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer. Neglected or improper maintenance can lead to increased friction, wear, and reduced energy transfer.
Best maintenance practices include:
- Scheduled inspections: Routine checks for gear wear, lubricant condition, and shaft alignment help identify issues early.
- Lubricant replacement: Timely replenishment prevents contamination and preserves low-friction operation.
- Component replacement: Worn bearings, seals, or gears should be replaced promptly to maintain optimal performance.
Consistent maintenance ensures long-term efficiency and reliability, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Load Distribution and Torque Handling
The way load is distributed across the gear teeth influences the efficiency of a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer. Uniform load distribution reduces localized stress and energy losses caused by uneven contact.
Key aspects of load distribution include:
- Pinion contact pattern: Proper tooth engagement distributes torque evenly.
- Bearing support: Strong bearings support radial and axial loads, minimizing gear deflection.
- Torque fluctuations: Smooth torque application reduces transient frictional losses.
Optimized load distribution allows the BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer to transmit power efficiently while preventing premature wear.
Industrial Applications and Relevance
Efficiency considerations vary depending on the application of the BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer. Common industries where efficiency is critical include:
| Industry | Application | Efficiency Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Material handling | Conveyor drives | Energy savings and reduced operating costs |
| Automotive | Steering systems and differential drives | Smooth torque transfer and minimal energy loss |
| Heavy machinery | Crushers, mixers, and presses | High torque demands with low heat generation |
| Robotics | Servo-driven systems | Precision and minimal backlash improve overall system efficiency |
Understanding the application ensures that the BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer is selected and maintained for maximum efficiency.
Summary
The efficiency of a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer is influenced by multiple interconnected factors:
- Design and gear geometry determine friction and smoothness of motion.
- Material selection and hardening affect wear resistance and contact precision.
- Lubrication and friction control minimize energy loss during operation.
- Operating conditions and load ensure the reducer operates within optimal parameters.
- Alignment and mounting reduce unnecessary mechanical resistance.
- Heat management prevents efficiency loss due to thermal effects.
- Maintenance practices sustain long-term performance.
- Load distribution and torque handling influence smooth energy transfer.
By addressing these factors systematically, industrial operators can maximize the performance, reliability, and energy efficiency of a BKM Hypoid Gear Reducer, ensuring it meets the demands of modern mechanical systems.
 05 Jun,2025
05 Jun,2025